The world is always in motion; it never stands still, constantly changing and developing. In the 21st century, these dynamics have been felt particularly in the rapid growth of technology and globalization, which has become an integral part of our lives. Each of us is faced daily with some or other aspects of technical progress and information exchange. In particular, the P2P sector, which is experiencing a sharp rise and intensive development over the last 4-5 years, it's rather an interesting area of research and investment. In this article, we will talk about the main issues of P2P security and the ways you should protect yourself in a network of this type.

Let’s Define the Concept
Answering a question of what is a peer to peer network, it is reasonable to start with its definition. This is a peer-to-peer communication protocol which characterized by more efficient use of the bandwidth of the signal transmission channel and high fault tolerance. The term was first used by IBM in networks with classical single-layer architecture and peer-to-peer workstations. It was used in the process of dynamic routing without the use of a server when each PC performed the function of both the client and the server.
What Is an Operation Principle of a Peer to Peer Network
Let’s find out in more detail what is the main working principle of peer to peer technology. This is the principle of decentralization; all nodes in the P2P network are equal. This idea forms the basis of blockchain technology which to date is very reliable and safe.
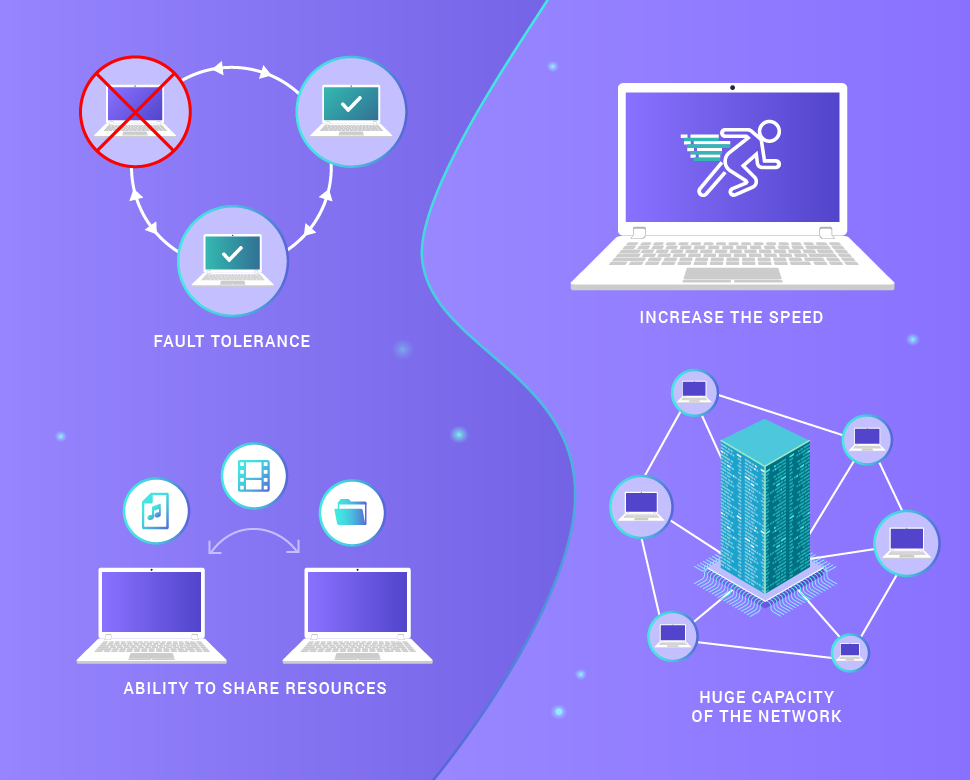
This approach provides such advantages over the client-server approach:
- fault tolerance in case of loss of communication with several network nodes,
- increases the speed of obtaining data by copying simultaneously from several sources,
- the ability to share resources without "binding" to specific IP addresses,
- the huge capacity of the network as a whole.
Currently, on the Internet more than half of all traffic is accounted for by the traffic of file-sharing P2P networks, and the largest of them exceeded the mark of one million concurrent nodes that separate petabytes (1015 bytes) of information. The total number of registered participants in P2P file-sharing networks around the world is about 100 million, and 28 millions of them share content every day.
The Sphere of Usage
Although P2P networks are now used mainly for file sharing, there are many other areas where this technology is also successfully applied. It includes:
- television and audio,
- parallel programming,
- distributed caching of resources to unload servers,
- distribution of notices and articles,
- support for the domain name system,
- indexing of distributed resources and their search,
- backup and creation of stable distributed data warehouses,
- message exchange,
- the creation of systems that are resistant to denial-of-service attacks,
- distribution of software modules.
There are a huge number of client programs for working with P2P networks, both commercial and open source. The work on improving the protocols, P2P security and increasing the functionality of the systems is constantly in progress.
In addition, CCTV cameras with P2P imaging technology (here you can find what is P2P camera and some info about its security) are used primarily in residential small and medium-sized private video surveillance systems, performing some functions of security systems and alarms. The P2P segment is one of the areas of alternative finance, based on lending to enterprises and individuals with the formal absence of an intermediary company.
Classification of P2P Applications
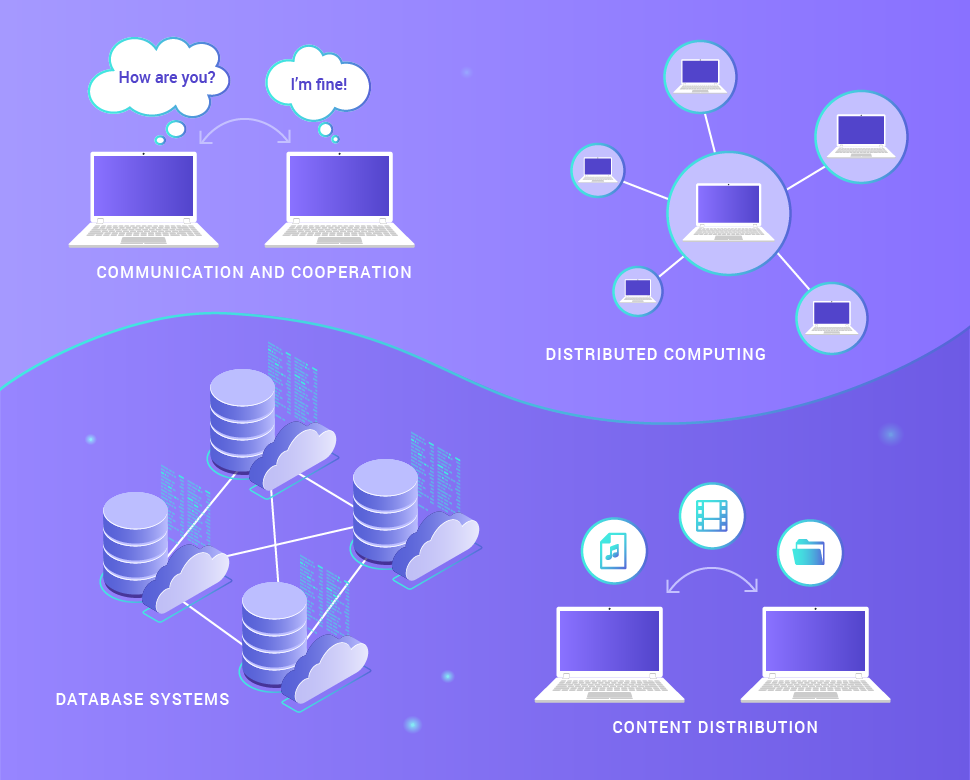
P2P architectures have been used for many applications of different categories. Here is how peer to peer applications can be classified.
- Communication and cooperation. This category includes systems that provide an infrastructure for direct, usually real-time, communications and peer-to-peer collaboration, for example, peer to peer application for chat and instant messaging.
- Distributed computing. The purpose of these systems is to combine the computing capabilities of peer-to-peer nodes to solve problems with intensive computations. To do this, the task is divided into a number of small subtasks, which are distributed to different nodes. The result of their work is then returned to the host.
- Database systems. Significant efforts were made to develop distributed databases based on the P2P infrastructure and increase P2P security. In particular, a local relational model was proposed that assumes that the set of all data stored in the peer to peer network consists of incompatible local relational databases in order to provide maximum security in them.
- Content distribution. This category includes most modern P2P networks, including systems and infrastructures designed to separate digital audiovisual information and other data between users.
How to Ensure Security in P2P Application Development?
The main requirement for any non-trivial P2P applications is the protection of data exchange between partners. The details of the protection depend on how the application is used and what exactly it needs to protect. There are three basic ways to ensure security - Identity protection, SSL and Blockchain, and the latter for now is the most reliable technology.
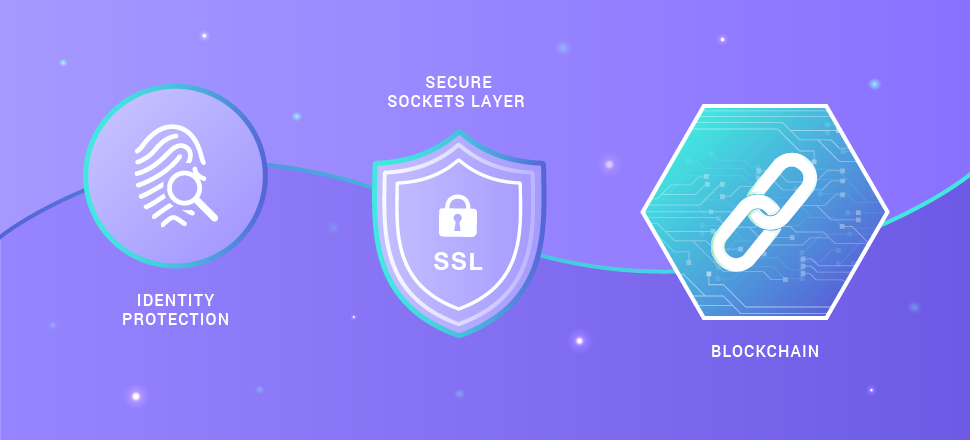
Identity Protection
The requirements for application security largely depend on how the application will be used and what needs to be protected. However, it is often possible to implement powerful protection using standard, "ready-made" technologies. An excellent example of this is identification.
SSL can be used both for server authentication and for client authentication using a similar mechanism. Typically, Web servers do not use SSL to authenticate clients, since it is easier to perform a password check. However, it is preferable to use transparent authentication of the client and the server made between the partners, using SSL, the one used in P2P applications.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
SSL is a secure protocol that ensures privacy when interacting with networks such as the Internet. SSL allows applications to interact without fear of spying and outside interference. When an application (client) wants to interact with another application (server), the client opens a socket connection to the server. The client and the server establish a secure connection. During this interaction, the server identifies itself to the client. If necessary, the client can also identify himself to the server. When authentication is complete and a secure connection is established, both applications can interact securely with each other.
Blockchain as the Main Tool to Ensure P2P Security
The blockchain is now quite popular, not only because it is used as a fundamental technology for creating and operating cryptocurrencies, but also as a tool that allows you to securely conduct online transactions using smart contracts, purchases and more.
As the name implies, blockchain is a series of blocks that write broker's blockchain data into a hash with reference to the block predecessor. Blocks are stored anonymously by all interested parties, which eliminates the centralized vulnerability points of cryptocurrency trading used by fraudsters.
The algorithm of work is always designed in such a way that everything around is not a trusting environment. Each P2P network node has its own Real-time database which constantly updates data and has a current data snapshot at the current time. Each of the nodes in the network offers its own block in a chain. Other nodes that are on the network do not trust it and start checking the block, comparing it with what they have in the datacast. If all network nodes accept a block, then it is recorded in a chain. All of these algorithms are described by the developer. Thus, it is believed that hacking, attacking the network is not possible, since it is stored on multiple nodes in the network. Thus, the security of operations within blockchain networks is ensured by the following factors.
- The system is decentralized;
- Reliability of encryption and validation algorithms;
- Blockchains can be private or public.
Within the blockchain network, operations are performed based on smart contracts. Smart contracts provide an opportunity to safely exchange money, shares, property and other assets directly, without the participation of intermediaries. All contracts are stored on the blockchain in encrypted form. Only the parties to the contract know about the conditions and subject of the contract, and no one can make changes to the program code. Transaction payments can be made in Bitcoin or Ethereum currency. Regarding the latter, we already have experience in developing such projects.
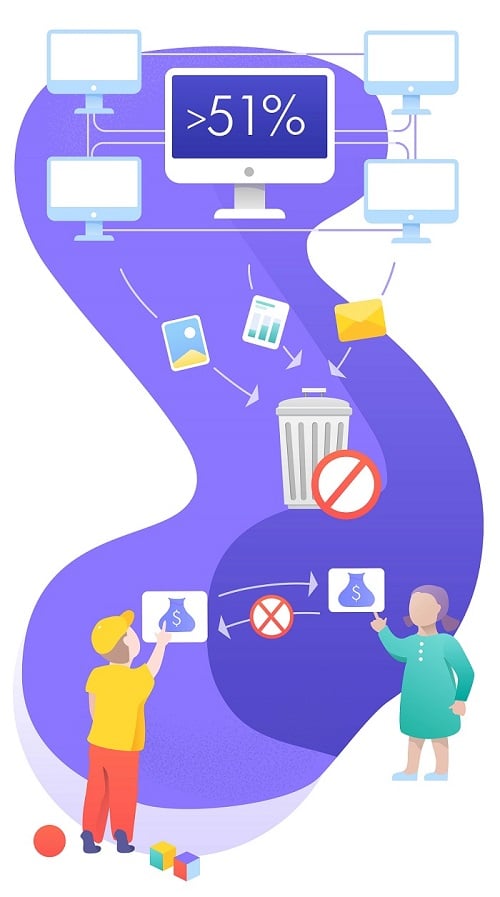
However, it is also worth mentioning what is a peer-to-peer main security risk.
- Establishment of the control over the network. This can happen if 51% or more of the capacity is concentrated in the hands of one person or group. As a result, all other participants will face a choice: to join the dominant structure and play by its rules or to leave the system.
- Without the right to oblivion. If the data is entered into the system based on the blockchain, the possibility of their deletion is questionable. Even though it is technically possible, the consequences of losing a huge amount of other data due to “rewinding” make the concept unrealizable.
- The reverse side of the immutability of information. The fact that the information already entered into the blocks of the chain cannot be changed or forged is one of the main values of the blockchain. Due to this, users can be sure that their transactions will be sent to the correct address, the balance on the crypto wallet will remain unchanged, etc. However, this “monolithic” reliability has a reverse side of the coin. For example, an inexperienced user may enter an erroneous address, and the money will be transferred to a completely different person or company. It is impossible to make a refund in this case.

Thus, it is certainly impossible to guarantee absolute secured peer to peer network, nor can it be done with respect to any other processes and technologies. However, there are ways to reduce your risks and the main ones are to be cautious with open data and carefully analyze the possible presence of fraud.





