In this article, you will learn how to test Web projects and mobile applications in our company.

Testing is conducted with the purpose to find program errors (bugs) before the users come across them.
We develop projects on the basis of the SCRUM methodology. The testing process is divided into two stages:
Testing in sprints (during the development process).
Testing after the development is completed (Final debugging).
The test automation engineer (quality assessment (QA) engineer) takes part in the sprint together with the developers. The time is allocated for checking the written code and correcting the errors found. It’s important to check the closed task on sprints. If you start to check the project only on completion of the programming (in our company the process lasts for 3-4 months), then you will find many errors. The closure of which can take up to 30-40 % of the development time. Checking the closed areas during the sprint reduces this percentage.
What is the final debugging?
Final debugging is testing all the elements of the system when the development of mobile apps is completed. Our team makes projects with client-server architecture, where exist different elements: back-end, frond-end, mobile clients, API, etc. When all the system entities are synchronized at the end of the project, errors can occur. Testing at the final debugging stage is a key process. Its task is to release a working system, where all elements work in accordance with the Technical Design Assignment.
Who conducts testing and at what stage?
Testing is carried out by the test automation engineer (hereinafter referred to as the QA). The QA is responsible for the quality of the product released. It’s the QA who makes a decision whether the product is ready to be released or not. The Company has established the standards of mobile app and Web project testing.
- In order to stay in the know of the project, the QA takes part in the stand-ups (meetings, gatherings) every day, as well as in the project demonstrations after the sprint is completed
- During the sprint process, the programmer closes the task and transfers it to the QA specialist.
- The QA checks the task and forms description of the problems related to it.
- The QA accompanies the bug till it’s closed.

To describe errors we use the bitbucket.org. service. Components of the problem description:
- Screen and page
- Version of the operating system (OS)
- Device
- App version
- Browser version
- Task framework (bug, task, offer).
- Bug criticality (blocking, critical, major (important) or minor (not important)).
- Screenshot, if available, or any other attached material (video, files loaded at the moment of testing).
- Step-by-step play back of the bug (in details, and with the conclusion of what is wrong, or the way it shall be, with reference to the Technical Design Assignment or Design).
To save time there are certain rules within the team. For example, a bug that has not been played back twice - cannot be placed. If the bug is not created in accordance with the standards, the task may not be accepted.
Testing types
Depending on the task, the QA specialist chooses the testing type, tools and degree of automation. It’s prepared as a test plan.
Degree of automation: manual testing, semiautomatic testing, automatic testing.
Testing types: acceptance testing, smoke testing, regression testing, beta testing.
The QA chooses the target of testing:
- Installation testing
- Functional testing
- Productivity testing (load testing, stability testing, volume testing)
- Stress-testing (fault detection and recovery testing)
- Usability testing
- User interface testing
- Safety testing
- Localization testing
- Compatibility testing
- Testing of the data and database integrity
Test plan
Before the testing starts, the QA prepares a test plan which includes:
UI testing,
UX testing,
load testing,
safety testing
After the preparations have been done, the QA embarks on playing back of the test cases described in the approved test plan.
Here is a sample of it:
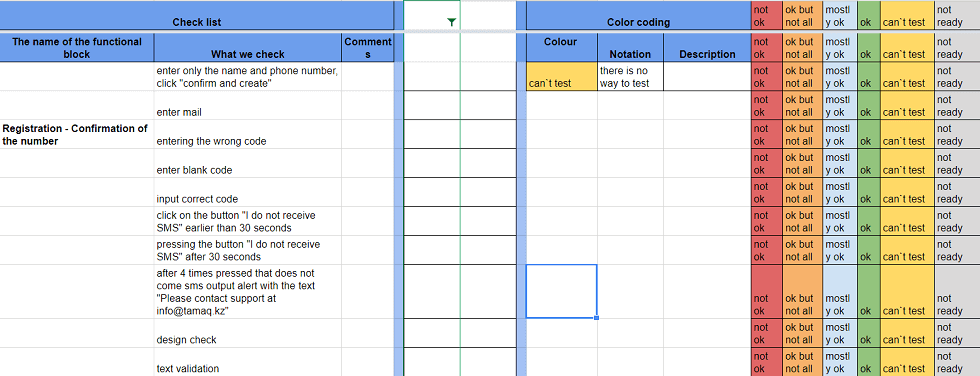
What do we check for the Web projects?
Usability:
The Website shall correspond to the design and prototype of the Website.
At the moment of the Website handover, the catalogue shall correspond to the one that exists in the prototype.
Comments relating to the convenience of the Website usage.
Things that were implemented in the project, but abnormally loading the system.
Website adaptability is checked. Such services as http://ipadpeek.com/ and http://screenqueri.es/ are used.
Download speed of the Website on different resolutions.
Load:
For load testing the following service is used: loadstorm.com
Load testing of API. It is conducted in case the Website uses inner or outer API.
Validity:
- We check the Website for the layout validity, we use the http://validator.w3.org/ resource.
Cross-Browser:
- We check the Website in all the supported browsers.
Safety:
We check the Website for presence of the malignant code: http://antivirus-alarm.ru/proverka/
We check the Website for vulnerability: http://find-xss.net/ we perform checking with the of sql injection scanner, xss scanner and find-link.
Download speed and Website operation speed:
We check the Website for the operating speed: https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/, according to the standards, the speed shall be 0.4 seconds.
We check the Website for broken links: http://anybrowser.com/linkchecker.html
As well as other parameters.
What do we check for the mobile applications?
- Usability
- Screen size
- telephone resources (memory leaks, power consumption)
- Screen resolutions and OS versions (OS versions, retina/non-retina displays, GPS, camera /lack of camera etc.)
- App response to the external interruptions
- In-app purchases
- Internationalization (checked in portrait and landscape modes)
- Constant feedback with the user (button’s response to the pressing, comments related to the faults)
- Updates
Requirements for preparation of the test plan
The QA prepares a complete test plan after the development has been finished, at the stage of preparing it for a complete testing of the project. The document shall describe the following points:
- The target of testing, task description.
- Description of the system components.
- Which entities are going to be tested during the test.
- Environment where the product under testing is.
- Description of the bottleneck places of the system.
- Procedure of the system testing (the list what order shall be used).
- Set of tools and its purpose (name of the tool and its application).
- Estimation by the time spent (list of estimation points).
- Types and proportion of testing (list of estimation in percentage form).
- Criteria of the product acceptance (allowable problems which don’t prevent the product from being released).
Test plan
The plan includes the following points:
- System elements
- Environment
- Testing documentation
- Testing principles
- Testing procedure
- Bottleneck in the design
- Dependency of the system entities
- Testing types
- Tools used
- Estimation by time
- Criteria of the product acceptance
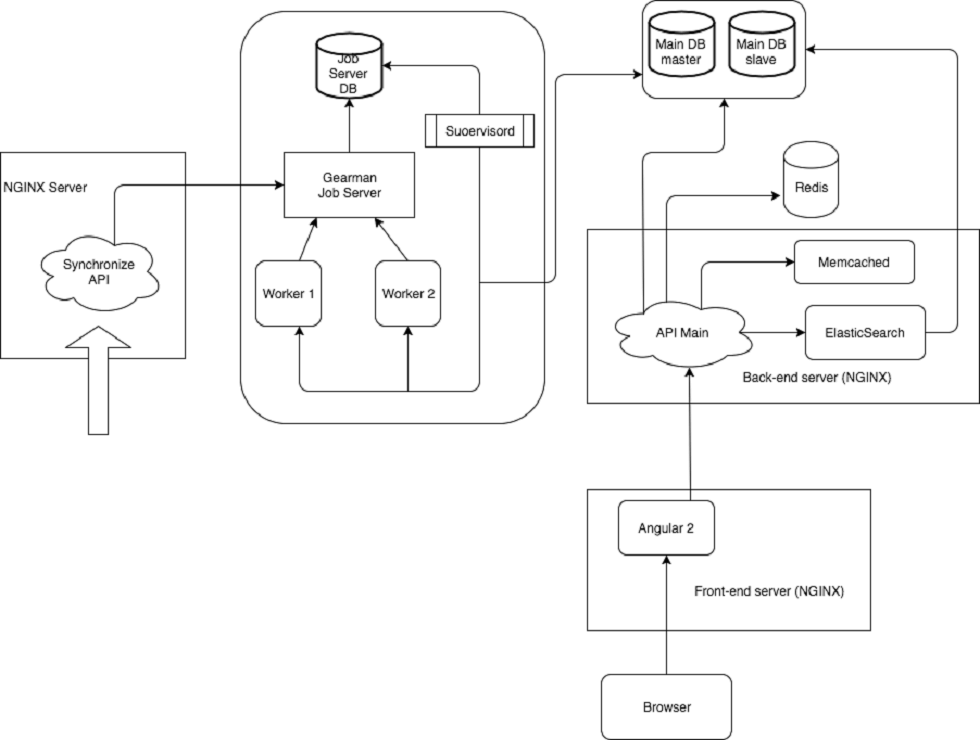


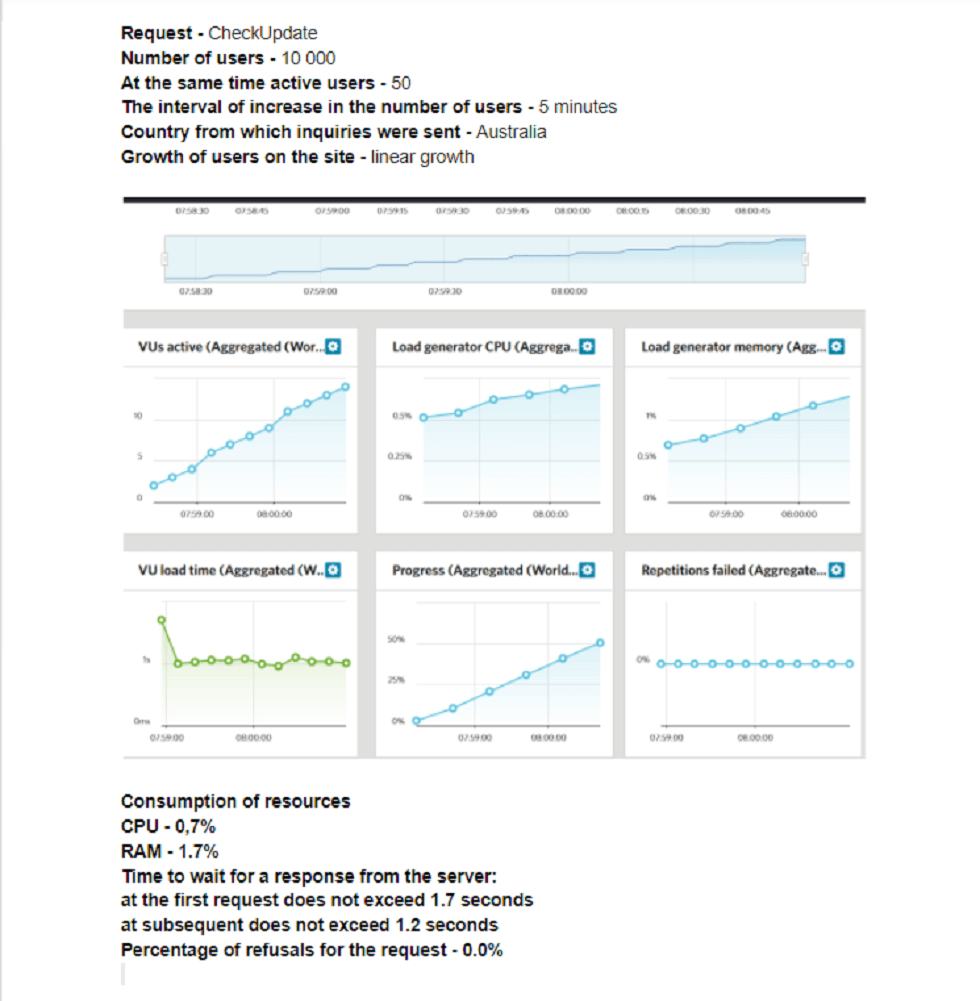
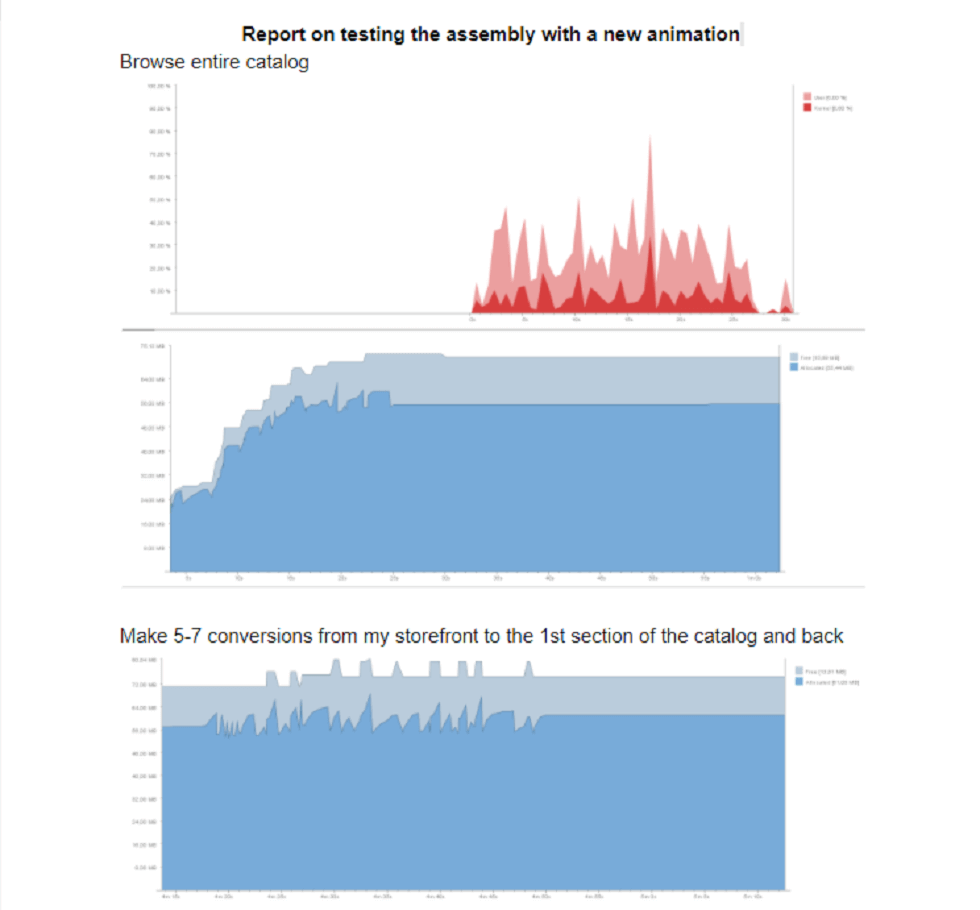
Report on the test result data
After the testing has been completed, a report is drawn up.
Work with development servers
There exist three servers in the project:
Dev – this server is used for development
Test – this server is under testing
Prod – this server is for the project release, only in the event it is ready.
The developer works and introduces corrections to the dev server. The QA conducts testing on the test server.
The testing process is inextricably linked with the development. In this article, we did not talk about testing automation and tools that speed up testing.
Checking tasks during the sprint, final debugging, drawing up a test plan, choosing the right type of testing and tools are the elements of successful project implementation.





